What Is Chicken Liver Nutrition?


Chicken liver nutrition has surged in popularity within many wellness circles, praised for its nutrient density and health benefits. Yet, there’s a deeper story to explore beyond the hype. Chicken liver, rich in essential nutrients such as iron, vitamin A, and B vitamins, offers more than just a nutritional powerhouse.
While some tout its benefits, diving into the nuances reveals a comprehensive view of how chicken liver can support overall wellness, shedding light on why it deserves attention in a balanced diet. With chicken liver nutrition gaining momentum, it’s important to peel back the layers and uncover the full spectrum of benefits and considerations this food offers.
What Is the Carnivore Diet?


The carnivore diet, centered on animal-based foods, presents a range of adaptations to meet various health objectives and personal preferences, each with distinct characteristics:
The Beef-Only Carnivore Diet
This variant focuses solely on beef consumption, appreciated for its straightforwardness and role in elimination diets. It’s an ideal starting point for individuals aiming to manage or alleviate autoimmune or chronic conditions. To ensure nutritional adequacy over time, it’s advisable to introduce a diverse selection of meats.
The Lion Diet
A more rigorous version, the lion diet limits intake to ruminant meats, salt, and water, serving as an effective elimination diet base with the option to gradually reintroduce other meats. This diet suits those seeking gut health and autoimmune condition improvements through a strict dietary framework.
The Nose-to-Tail Carnivore Diet
Advocating for the consumption of the entire animal, including organ meats, this variation aims for a rounded nutrient profile. However, it’s important to monitor liver and kidney intake to avoid possible vitamin A toxicity and other nutrient imbalances, especially in individuals with specific health conditions.
The Meat Only Carnivore Diet
Expanding to include all types of muscle meat from the animal kingdom while excluding organ meats, dairy, and eggs, this method is perfect for those pursuing a basic elimination diet and have no issues with muscle meats.
The Zero-Carb Carnivore Diet
Targeting foods with minimal to no carbohydrates, this diet includes dairy, eggs, and all meats, focusing on meat and animal fats. It accommodates those without autoimmune or severe chronic health concerns who can tolerate dairy and/or eggs.
The Carnivore Keto Diet
Merging ketogenic diet principles with the carnivore lifestyle, this low-carb, high-fat approach seeks to replicate fasting benefits and introduces more diet variety with low-toxicity plant foods such as avocados and coconut oil. It’s suited for metabolically healthy individuals who have resolved or nearly resolved their chronic health conditions.
The Carnivore-ish Keto Diet
Offering greater flexibility, this variation incorporates additional ketogenic elements while prioritizing animal-based foods. It includes alternative keto sweeteners, selected nut products, and other keto-friendly items for those who are metabolically stable, have recovered from health issues, and do not struggle with food addiction.
Animal-Based Diet
A less restrictive option, focusing primarily on animal products but permitting fruits, honey, and raw dairy. Based on our clinical experience, only individuals with exceptional metabolic flexibility and elite athletes thrive on this diet. We generally do not recommend this variation generally because of the risks of mixing fruit with high fat.
Each of these carnivore diet variations caters to different dietary needs and health goals, offering a spectrum of choices for those looking to start on or modify their carnivore diet journey.
What Are the Benefits of the Carnivore Diet?
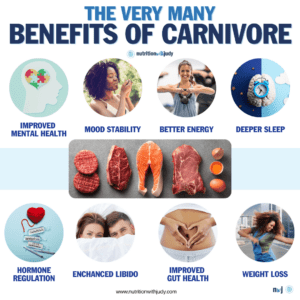

The carnivore diet has many incredible health benefits. In our clinical experience, we have found that this diet offers numerous advantages, ranging from improved digestive health to enhanced mental clarity. Here is a summary of some of the benefits associated with adopting a carnivore diet.
1. Simplified Nutrition: One of the most appealing aspects of the carnivore diet is its simplicity. With a focus solely on animal products, individuals find meal planning and preparation less time-consuming and more straightforward. This diet eliminates the need to track various vitamins and minerals found in a wide range of plant foods, as animal products alone can provide all essential nutrients in bioavailable forms.
2. Enhanced Digestive Health: Many people turn to the carnivore diet to alleviate digestive issues. The elimination of fiber-rich plant foods can lead to reduced bloating, gas, and inflammation in the gut for some individuals. Since animal products are efficiently digested and absorbed, this diet can minimize digestive stress, offering relief to those with sensitivities or intolerances to certain plant compounds.
3. Weight Loss and Improved Body Composition: The high protein and fat content of the carnivore diet can enhance satiety, leading to reduced calorie intake without the need for deliberate restriction. Protein is also crucial for muscle repair and growth, which, coupled with the diet’s potential to reduce body fat, can result in improved body composition.
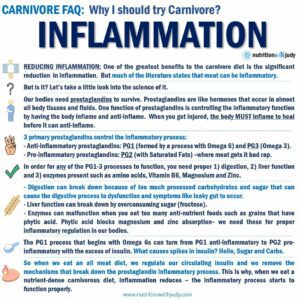

4. Reduced Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a root cause of many diseases, and the carnivore diet’s elimination of processed foods and plant-based anti-nutrients that can trigger inflammation in some individuals (such as lectins, gluten, and phytates) may lead to decreased inflammation markers. This can contribute to overall better health and reduced risk of chronic conditions.
5. Better Mental Health and Cognitive Function: In our clinical practice, we have seen positive effects on mental health and cognitive function. The diet’s high content of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins B12 and D, and minerals such as zinc and iron, all crucial for brain health, could explain these benefits. Some individuals report improved mood, increased mental clarity, and enhanced focus.
6. Regulation of Blood Sugar and Improvement in Metabolic Health: By eliminating carbohydrates, the carnivore diet can stabilize blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome, as it can aid in the management and potentially the reversal of these conditions.


7. Potential to Alleviate Autoimmune and Skin Disorders: The carnivore diet can help reduce symptoms of autoimmunity and skin disorders such as eczema, psoriasis, and rheumatoid arthritis. The removal of dietary triggers found in plant foods can support the immune system’s normalization, reducing autoimmune reactions and skin inflammation.
The carnivore diet presents a strong option for individuals seeking to simplify their nutrition, improve digestive health, lose weight, reduce inflammation, enhance mental function, stabilize blood sugar levels, and potentially alleviate symptoms of autoimmune and skin disorders. The carnivore diet provides a strong foundation for anyone wanting to begin this way of eating.
What Are the Values Behind Chicken Liver Nutrition?


Chicken liver is a powerhouse of nutrition, densely packed with essential nutrients that play important roles in maintaining and enhancing health. Within a modest serving of 2 ounces, chicken liver provides a remarkable spectrum of vitamins and minerals, each contributing to various health benefits.
One of the standout nutrients in chicken liver is vitamin A, with a 2-ounce serving offering about 11,000 IU. Vitamin A is vital for maintaining healthy vision, supporting immune function, and ensuring the normal functioning of the heart, lungs, and kidneys. Additionally, chicken liver is an excellent source of B vitamins, particularly vitamin B12, with a 2-ounce serving containing upwards of 16 mcg. Vitamin B12 is essential for nerve tissue health, brain function, and the production of red blood cells.
Iron is another major nutrient found abundantly in chicken liver, with a 2-ounce serving providing about 5 mg. This mineral is key for forming hemoglobin, which transports oxygen in the blood, and supports energy production and metabolism. Chicken liver also boasts significant amounts of folate (about 400 mcg per 2 ounces), crucial for DNA synthesis and preventing neural tube defects during pregnancy.
Furthermore, chicken liver is a good source of zinc and selenium. Zinc, with about 2 mg in a 2-ounce serving, supports immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. Selenium, around 20 mcg per serving, plays a critical role in metabolism and thyroid function, and acts as a powerful antioxidant to combat oxidative stress.
Chicken liver offers a concentrated source of vitamins A, B12, folate, and minerals such as iron, zinc, and selenium, each contributing to essential bodily functions ranging from vision and brain health to oxygen transport, immune defense, and metabolic efficiency.
The Risks of Overconsuming Chicken Liver
While chicken liver is acclaimed for its rich nutrient profile, offering a myriad of health benefits, overconsumption poses potential risks, notably vitamin A toxicity. Chicken liver contains significant amounts of vitamin A, a fat-soluble vitamin essential for vision, immune function, and skin health. However, its lower vitamin A content compared to beef liver means the risk of toxicity is reduced, though not eliminated. Two ounces of chicken liver provide around 11,000 IU of vitamin A, surpassing the recommended daily intake for adults, which stands at 900 mcg (3,000 IU) for men and 700 mcg (2,300 IU) for women.
Vitamin A toxicity can lead to symptoms such as headache, nausea, dizziness, and in severe cases, liver damage and neurological issues. Therefore, it’s important for individuals incorporating chicken liver into their diet to consume it in moderation, balancing their intake with other foods to prevent excessive accumulation of vitamin A. Opting for chicken liver allows individuals to enjoy the nutritional benefits of organ meats while minimizing the risk of toxicity, but mindfulness regarding quantity remains essential for maintaining health and avoiding adverse effects.
Should I Eat Chicken Liver In My Carnivore Diet?


Incorporating chicken liver into a carnivore diet should be a decision based on personal preference and enjoyment rather than a perceived obligation. While chicken liver is nutrient-rich, offering a unique blend of vitamins and minerals beneficial for health, it’s essential to consider that nutritional adequacy on a carnivore diet can be achieved without the inclusion of organ meats. We advocate for consuming chicken liver only if you genuinely enjoy its taste and texture, and in proportions that reflect the natural composition of the animal, suggesting a moderate and balanced approach to organ meat consumption.
Forcing yourself to eat chicken liver, or any organ meat for that matter, if you dislike its flavor or texture, is unnecessary and can take away from the pleasure and sustainability of your diet. Similarly, investing in expensive desiccated organ supplements may not be the best use of resources, especially considering many individuals thrive on the carnivore diet without consuming any organ meats.
The key to a successful carnivore diet lies in focusing on foods that you enjoy and that make you feel your best, whether that includes organ meats such as chicken liver or consists solely of muscle meats and other animal-based foods.
Sourcing Chicken Liver
When including organ meats, particularly liver, into your diet, the emphasis on sourcing the highest quality available cannot be overstated. The liver, a vital organ for detoxification, processes and neutralizes toxins from the body. Consequently, the quality of the liver you consume directly impacts the purity and nutritional value of the organ meat on your plate. Pasture-raised sources are highly recommended as they are less likely to be exposed to high levels of contaminants and potentially harmful feed ingredients, such as antibiotics and hormones, commonly found in conventional farming practices.
Opting for corn and soy-free chicken liver is also advisable if possible. Chickens raised without these common feed ingredients are generally healthier and their livers are less burdened by toxins, making the liver you consume safer and more nutritious. While it might require more effort or expense to source such high-quality organ meats, the health benefits far outweigh the inconvenience.
High-quality chicken liver not only offers a richer nutrient profile, including essential vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids, but also ensures you’re minimizing your intake of unwanted chemicals and toxins. Investing in the best quality liver available is a wise choice for those seeking to maximize the health benefits of their carnivore diet while minimizing potential risks associated with toxin exposure.
Closing Thoughts On Chicken Liver Nutrition and the Carnivore Diet
Chicken liver offers a nutritional powerhouse within the carnivore diet, packed with essential nutrients such as vitamin A, B vitamins, and iron. These nutrients support a range of bodily functions from vision and immune health to aiding in metabolic processes and red blood cell formation. However, moderation in consumption is key due to the risk of vitamin A toxicity, especially since chicken liver, while lower in vitamin A compared to beef liver, still contains high levels of this nutrient. Consuming in moderation helps mitigate the risk of adverse effects such as headache, nausea, and more serious health issues over time.
When incorporating chicken liver or any organ meats into the diet, prioritizing high-quality sources is crucial. Pasture-raised, corn, and soy-free options are ideal, minimizing exposure to toxins that the liver may accumulate, thus ensuring a cleaner and more beneficial nutrient intake. This emphasis on quality sourcing aligns with the carnivore diet’s principles of consuming nutrient-dense, minimally processed foods for optimal health.
Overall, chicken liver can be a valuable addition to a carnivore diet when enjoyed in moderation and sourced from high-quality, pasture-raised environments, offering profound nutritional benefits while maintaining health and wellness considerations.
Work With Our Trusted Carnivore Diet Functional Nutritional Therapy Practitioners
The Nutrition with Judy practice is honored to be a trusted carnivore diet practitioner support serving clients from around the globe. We’re passionate about helping our clients achieve root-cause healing in order to lead the best quality of life possible that’s nearly symptom-free. Our team is dedicated to providing the important nuances behind consuming organ meats. We welcome you to explore our free resources and are always available to support you through personalized protocols. Our Symptom Burden Assessment (SBA) is the perfect starting point for discovering your root cause and is required to work with our team— you can learn more in-depth about this powerful tool here.
Start your root-cause healing journey today and contact us any time with any questions or concerns.
DISCLAIMER: This content is for educational purposes only. While we are board-certified in holistic nutrition and are nutritional therapy practitioners, we are not providing medical advice. Whenever you start a new diet or protocol, always consult with your trusted practitioner first.