
What Are the Foods With No Sugar?


Understanding the foods that contain no sugar is crucial for individuals following ketogenic diets and those starting on the journey of reintroducing foods into a carnivore diet. This knowledge helps support metabolic health by maintaining stable blood sugar levels but also enhances the effectiveness of these diets in achieving weight loss, improving energy levels, and reducing inflammation.
For those on a ketogenic diet, identifying sugar-free foods helps in staying within the low-carb threshold, while carnivore dieters can use this information to make informed choices during the reintroduction phase, ensuring they continue to reap the benefits of their dietary regimen.
What Is the Carnivore Diet?
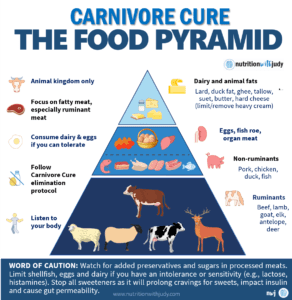

The carnivore diet, centered on animal-based foods, offers various plans to meet personal health objectives, each with distinctive benefits:
The Beef-Only Carnivore Diet
Focuses solely on beef for its simplicity and effectiveness, especially recommended for those dealing with autoimmune or chronic conditions. It’s a solid starting point, though diversifying meat sources is advised for long-term nutritional balance.
The Lion Diet
This stricter version limits intake to ruminant meats, salt, and water, ideal for elimination diets and those focusing on autoimmune and gut health.
The Nose-to-Tail Carnivore Diet
Encourages consuming the entire animal, including organ meats, to maximize nutrient intake, with caution advised for liver and kidney consumption due to potential nutrient imbalances, especially vitamin A toxicity.
The Meat-Only Carnivore Diet
Includes all types of muscle meat, excluding organ meats, dairy, and eggs, suitable for those on a foundational elimination diet who tolerate muscle meat well.
The Zero-Carb Carnivore Diet
Emphasizes foods with minimal carbohydrates, incorporating dairy, eggs, and all meats, with an option to add seasonings, recommended for those without autoimmune or deeper chronic health issues and who tolerate dairy and eggs.
The Carnivore Keto Diet
A low-carb, high-fat option that blends ketogenic diet principles with carnivore diet, including low-toxicity keto foods such as avocados and coconut oil, suited for metabolically healthy individuals with resolved chronic health issues.
The Carnivore-Ish Keto Diet
Offers more flexibility by integrating additional ketogenic elements while focusing on animal-based foods, ideal for metabolically healthy individuals without food addiction issues.
Animal-Based Diet
Expands on the carnivore diet by including fruits, honey, and raw dairy, observed to usually only benefit highly metabolically flexible individuals and elite athletes in clinical practice. We generally don’t recommend this variation due to the risks of mixing high fat and fruit together.
Each variation of the carnivore diet is designed to cater to different health goals and dietary preferences, ensuring there’s a suitable option for everyone interested in pursuing a diet focused on meat-based nutrition.
What Are the Benefits of the Carnivore Diet?
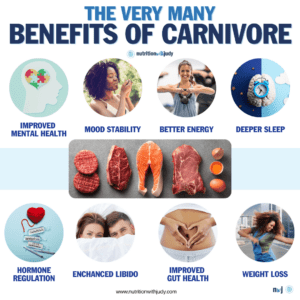

The carnivore diet presents a myriad of health benefits that attract individuals seeking alternative dietary strategies for wellness and disease management. This high-protein, high-fat, virtually zero-carb diet has gained attention for its simplicity and effectiveness in addressing a wide range of health issues, from autoimmune disorders to metabolic syndrome. Let’s take a closer look at the benefits of adopting a carnivore lifestyle.
Nutritional Completeness


Animal products provide all essential nutrients in bioavailable forms, including vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and fatty acids, important for optimal health. Unlike plant-based foods, meat offers a complete protein profile, essential fats such as omega-3s, and nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, and zinc without the need for supplementation.
Digestive Health
The carnivore diet can lead to improvements in digestive health by eliminating dietary fibers and antinutrients found in plant foods, which some individuals find hard to digest. This reduction can alleviate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), bloating, and inflammation, promoting a healthier gut microbiome.
Autoimmune and Inflammatory Conditions


By excluding potential dietary triggers such as gluten, lectins, and nightshades, the carnivore diet reduces inflammation and supports the management of autoimmune diseases. In our clinical experience, this diet can lead to symptom remission in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease.
Weight Loss and Metabolic Health
The diet’s low carbohydrate content can induce a state of ketosis, where the body burns fat for fuel instead of glucose, leading to weight loss and improved metabolic markers. This shift can enhance insulin sensitivity, reduce blood sugar levels, and lower the risk of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Mental Clarity and Mood Improvement


In our clinical experience, we have found clients have improved mental clarity, focus, and mood stabilization on the carnivore diet. This is partially due to stable blood sugar levels and the high content of omega-3 fatty acids, known for their anti-inflammatory effects on the brain, and can contribute to cognitive benefits.
Simplicity and Satiety
The carnivore diet is straightforward, eliminating the need for complex meal planning or calorie counting. High in protein and fats, it promotes satiety, potentially reducing overall calorie intake without the sensation of hunger or deprivation often associated with other diets.
Physical Performance and Recovery


The high protein content supports muscle maintenance and growth, making the diet popular among athletes and those looking to improve physical performance and recovery. The diet’s anti-inflammatory nature can also reduce recovery times.
Why Should We Limit Our Sugar Intake?
Limiting sugar intake is most important for maintaining optimal health and preventing a myriad of health issues associated with overconsumption. Sugar, particularly in its refined form, is greatly present in modern diets, hidden in various foods from breakfast cereals to sauces, contributing to excessive daily intake far beyond recommended levels. This overindulgence in sugar has been linked to numerous health consequences, emphasizing the importance of moderation.
You can learn more in-depth about the dangers of sugar here.
Increased Risk of Obesity
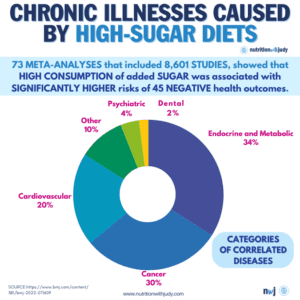

Sugar is a major contributor to the obesity epidemic facing many countries. High in calories and low in nutritional value, sugary foods and beverages can lead to weight gain and obesity when consumed in excess. Obesity, in turn, increases the risk of developing chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
Type 2 Diabetes
Consuming too much sugar can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. Over time, this can escalate to type 2 diabetes, characterized by high blood sugar levels. Managing sugar intake is crucial for preventing and managing this condition.
Heart Disease
Studies have shown a direct correlation between high sugar intake and an increased risk of heart disease. Excessive sugar consumption can lead to obesity, inflammation, high triglyceride levels, and hypertension, all of which are risk factors for heart disease.
Dental Health
Sugar is a leading cause of dental problems, including cavities and gum disease. Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugar, producing acids that can erode tooth enamel, leading to dental decay.
Mental Health
There’s growing evidence linking high sugar consumption with mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can impact mood, leading to mood swings and a higher risk of mood disorders.
Cognitive Decline
Excessive sugar intake has also been associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline, including conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease. High sugar levels can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, which are detrimental to brain health.
Liver Damage
Sugar, specifically fructose, is metabolized by the liver. Overconsumption can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition characterized by excessive fat buildup in the liver, leading to inflammation and liver damage.
Aging
Sugar can accelerate the aging process, contributing to the development of wrinkles and a loss of skin elasticity. This is due to the process of glycation, where sugar molecules attach to proteins in the skin, damaging collagen and elastin.
Understanding Carbohydrates In the Body
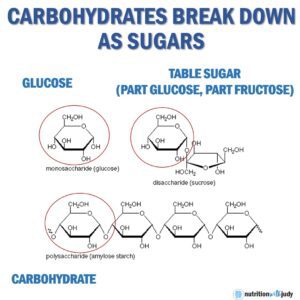

Carbohydrates, considered the only unessential macronutrients, undergo a complex process of digestion and metabolism, ultimately breaking down into glucose, which serves as a primary energy source for the body. This process begins in the mouth, where enzymes in saliva start breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars. As these carbohydrates move through the digestive system, they are further broken down in the small intestine by additional enzymes. The end products of this digestion are simple sugars, primarily glucose, which are then absorbed through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream.


Once in the bloodstream, glucose can be used immediately for energy or stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen for later use. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a key role in the regulation of blood glucose levels, facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells throughout the body. When glycogen storage reaches its capacity, excess glucose can be converted into fat for long-term storage, contributing to weight gain and associated health issues if not managed properly.
Given this metabolic pathway, it’s essential to understand that all consumed carbohydrates—whether from starchy foods, sugars, or fiber—impact glucose levels in the body. Therefore, individuals should consider their total carbohydrate intake as part of their sugar intake. Monitoring and managing carbohydrate consumption is important for maintaining stable blood glucose levels, which can help in the prevention and management of metabolic diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
We need to be mindful of both the quantity and quality of carbohydrates consumed and whether they should be reintroduced to your carnivore diet.
Foods With No Sugar


Foods with no sugar should be emphasized for individuals following low-carb, ketogenic, or carnivore diets, and for those aiming to reduce their sugar intake for health reasons. These foods help stabilize blood sugar levels, support weight management, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases associated with high sugar consumption. Here’s a list of foods that contain no or negligible sugar:
- Meat: Beef, pork, lamb, and game meats are naturally sugar-free and provide high-quality protein and essential nutrients.
- Poultry: Chicken, turkey, and duck are excellent sources of protein without any sugar content.
- Fish and Seafood: All types of fish and seafood, including salmon, trout, sardines, and shrimp, are free of sugar and rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Eggs: Eggs are a versatile, nutrient-dense food with no sugar, offering a good balance of protein and fats.
- Dairy: Certain dairy products, particularly hard cheeses and butter, have minimal to no carbohydrates or sugars. However, it’s important to check labels as some dairy products can contain added sugars.
- Fats and Oils: Pure fats and oils, such as olive oil, coconut oil, and avocado oil, are free from sugars and carbohydrates.
- Non-Starchy Vegetables: Leafy greens (spinach, kale), cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower), and other non-starchy vegetables are low in sugar and carbohydrates, making them suitable for a low-sugar diet. Be aware of plant anti-nutrients found in these foods and be mindful when considering reintroducing these on a carnivore diet.
Foods With No Carbs


Identifying foods that contain no carbohydrates is essential for individuals following a ketogenic, carnivore, or other low-carb diets, focusing on minimizing carb intake for health or weight management goals. Here is a list of foods that typically contain zero (or virtually zero) carbohydrates, making them ideal for such dietary plans:
- Meats: All unprocessed meats, including beef, pork, lamb, and game meats, contain no carbs and are rich in protein and fats.
- Poultry: Chicken, turkey, and duck are carb-free when unprocessed and without added ingredients.
- Fish and Seafood: Fresh fish and seafood, such as salmon, trout, shrimp, and shellfish, are free of carbohydrates.
- Eggs: Eggs have less than 1 gram of carbs each, making them an excellent low-carb food.
- Most Cheeses: Hard and semi-hard cheeses, including cheddar, gouda, and parmesan, have negligible carbohydrates.
- Butter and Most Fats: Pure fats, including butter, ghee, olive oil, and coconut oil, are carb-free.
- Certain Condiments: Specific condiments, such as mustard and many types of vinegar (excluding balsamic), contain no carbs.
The Carnivore Diet for Addressing Excessive Sugar Consumption
We believe that the carnivore diet stands out as the front-runner in dietary approaches to counteract the adverse effects of excessive sugar consumption, offering a unique pathway to mitigate chronic illnesses linked to high sugar intake and aiding in overcoming sugar addiction.
By fundamentally eliminating carbohydrates and focusing primarily on animal-based foods, the carnivore diet directly tackles the root cause of sugar-related health issues. It naturally stabilizes blood sugar levels by bypassing the consumption of sugars and carbohydrates, which are the primary drivers of insulin resistance, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. This stabilization is crucial for individuals struggling with diabetes and other metabolic conditions exacerbated by fluctuating blood sugar levels.
The carnivore diet’s restriction of carbohydrate intake helps in reducing inflammation, a common consequence of chronic diseases associated with excessive sugar consumption. The high intake of quality proteins and fats on this diet not only supports bodily functions and muscle maintenance but also promotes satiety. This aspect is particularly beneficial for addressing sugar addiction, as it diminishes cravings and the cyclical nature of compulsive sugar consumption by providing consistent energy levels and reducing the psychological urge to reach for sugary foods.
The carnivore diet offers a therapeutic dietary strategy that not only aids in managing and potentially reversing the consequences of excessive sugar intake but also supports the healing process from sugar addiction, contributing to overall health and wellness. You can learn more about the specific mechanisms here.
Closing Thoughts On Foods With No Sugar and the Carnivore Diet
Throughout our exploration of foods with no sugar and the carnivore diet, we’ve highlighted key insights for individuals aiming to improve their health through dietary adjustments. Foods devoid of sugar, including meats, poultry, fish, seafood, eggs, certain dairy products, and pure fats, are foundational in diets targeting blood sugar stabilization, weight management, and the reduction of chronic disease risks. These foods are particularly emphasized in the carnivore diet, a regimen that eliminates carbohydrates entirely, focusing on animal-based nutrition.
The carnivore diet addresses the negative impacts of excessive sugar consumption by stabilizing blood sugar levels, reducing inflammation, and supporting the management of chronic illnesses related to sugar overindulgence. Furthermore, it provides a viable solution for breaking the cycle of sugar addiction, offering satiety and reducing cravings through its high protein and fat content.
This diet brings out the importance of quality, nutrient-dense foods in achieving overall health and well-being, presenting a simplified yet effective dietary approach for those seeking to diminish the consequences of a high-sugar lifestyle and embrace a healthier eating pattern.
Work With Our Trusted Carnivore Diet Functional Nutritional Therapy Practitioners
The Nutrition with Judy practice is honored to be a trusted carnivore diet practitioner support serving clients from around the globe. We’re passionate about helping our clients achieve root-cause healing in order to lead the best quality of life possible that’s nearly symptom-free. Our team is dedicated to helping our clients personalize their carnivore diet for optimal health results. We welcome you to explore our free resources and are always available to support you through personalized protocols. Our Symptom Burden Assessment (SBA) is the perfect starting point for discovering your root cause and is required to work with our team— you can learn more in-depth about this powerful tool here.
Start your root-cause healing journey today and contact us any time with any questions or concerns.
DISCLAIMER: This content is for educational purposes only. While we are board-certified in holistic nutrition and are nutritional therapy practitioners, we are not providing medical advice. Whenever you start a new diet or protocol, always consult with your trusted practitioner first.